Top Wheat Producing Countries
Sign up for Ag Commodities Focus: Stay ahead of the curve on ag commodities trends.
According to the latest statistics from the USDA, below are the top wheat producing countries in 2023/2024 (figures in metric tons):
- China: 136.59 million
- European Union: 134.15 million
- India 110.55 million
- Russia 91.5 million
- United States 49.31 million
- Canada 31.95 million
- Pakistan 28.18 million
- Australia 26 million
- Ukraine 23 million
- Turkey 20 million
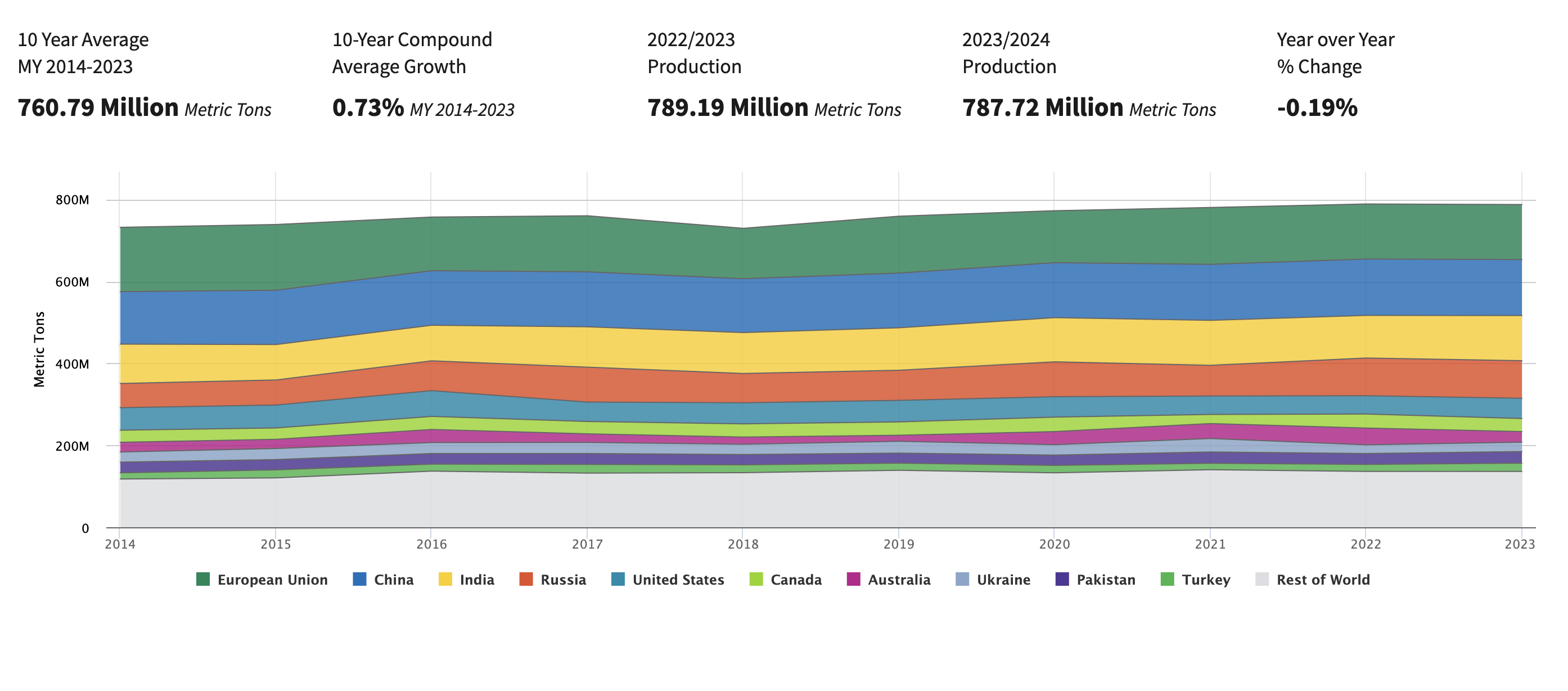
Chart: Wheat Production Trend, 2014 - 2023
What Are the Challenges Faced by Wheat Producing Countries?
The main challenges faced by wheat-producing countries include the following:
Climate Change
Rising temperatures, drought, and erratic rainfall patterns pose a significant threat to wheat production globally. These climatic changes can lead to reduced yields and crop failures.
Wheat is particularly vulnerable to heat stress during the grain-filling stage, which can severely impact grain quality and quantity.
Water Scarcity
Wheat cultivation requires substantial amounts of water, and many major wheat-growing regions face water scarcity issues.
Drought conditions can severely limit wheat yields, especially in regions with limited irrigation infrastructure.
Soil Degradation
Intensive farming practices, overgrazing, and deforestation can lead to soil erosion, nutrient depletion, and loss of soil fertility, negatively impacting wheat productivity.
Pests and Diseases
Wheat is susceptible to various pests, such as insects (e.g., aphids, stem borers) and diseases (e.g., rust, blight), which can cause significant yield losses if not properly managed.
The emergence of new pest and disease strains poses an ongoing challenge for wheat breeders and farmers.
Fertilizer and Input Costs
The rising costs of fertilizers, pesticides, and other agricultural inputs can strain the profitability of wheat production, especially for smallholder farmers.
Trade Disruptions
Conflicts, political tensions, and trade barriers can disrupt the global wheat trade, leading to supply shortages and price volatility, as seen with the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Increasing Demand
The growing global population and changing dietary preferences are driving up the demand for wheat, putting pressure on producing countries to increase yields sustainably.
Processing Contaminants
Certain contaminants, such as acrylamide, can form during high-temperature processing of wheat products, posing food safety concerns and requiring careful monitoring.
How Does Wheat Production Impact the Economy of These Countries
Wheat production plays a significant role in the economies of major wheat-producing countries in several ways:
Contribution to Agricultural Output and GDP
For countries like India, Russia, and Pakistan, wheat is a major agricultural crop, and its production contributes substantially to the overall agricultural output and GDP.
In India, wheat accounts for around 12% of the total value of agricultural output, making it a crucial component of the agricultural economy.
In Russia, wheat production contributes over 2% to the country's GDP, highlighting its economic importance.
Employment Generation
The wheat production sector generates employment opportunities for a significant portion of the rural population in major producing countries like China, India, and Pakistan.
This includes jobs in cultivation, harvesting, transportation, storage, and processing of wheat.
Food Security
Wheat is a staple food grain, and its domestic production plays a vital role in ensuring food security for the populations of major producing countries.
Countries like China and India rely heavily on domestic wheat production to meet the food demands of their large populations.
Export Earnings
Major wheat exporters like Russia, Canada, and Australia generate significant export earnings from wheat trade, contributing to their overall trade balances and foreign exchange reserves.
For example, wheat exports account for around 3.5% of Russia's total export earnings.
Input Industries
Wheat production supports various input industries, such as fertilizers, pesticides, farm machinery, and irrigation equipment, contributing to their growth and employment generation.
Pricing and Inflation
Fluctuations in wheat production can impact domestic wheat prices, which in turn can influence overall food inflation rates, affecting the cost of living and real incomes of the population.
Rural Development
In many wheat-producing countries, the crop is cultivated predominantly by small and marginal farmers, and its production plays a crucial role in rural development and poverty alleviation programs.